Improving Website Performance with Efficient CSS
Написана давно - Время чтения: 8 минуты
Уроки CSS
Веб-разработка является одним из самых популярных направлений в IT сфере. Создание стильных и функциональных веб-сайтов требует знания нескольких языков программирования, включая HTML, CSS и JavaScript. В этой статье мы рассмотрим важные уроки по работе с CSS, который отвечает за структуру и внешний вид веб-сайта.
Minimizing CSS file size
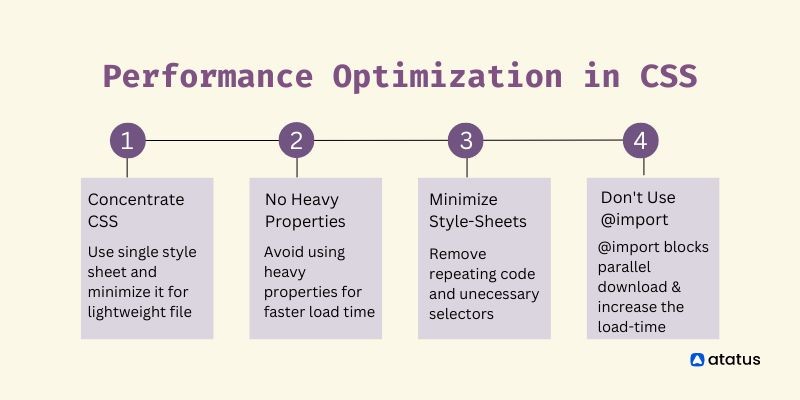
Одним из ключевых аспектов работы с CSS является оптимизация размера файлов. Увеличение размера CSS файлов может привести к повышенному времени загрузки веб-страницы, что может негативно повлиять на пользовательский опыт. Ниже приведены некоторые методы минимизации размера CSS файлов:
- Использование сокращенных свойств: В CSS существуют сокращенные свойства, которые позволяют задавать несколько значений одновременно. Например, вместо написания двух отдельных свойств font-style и font-weight можно использовать font: italic bold;
- Удаление ненужных символов: При написании CSS кода избегайте лишних пробелов, отступов и комментариев, так как они увеличивают размер файла без добавления функциональности.
- Минимизация файлов: Существуют специальные инструменты, которые позволяют автоматически минимизировать CSS файлы путем удаления пробелов и комментариев. Такие инструменты помогают сократить размер файла в несколько раз.
- Использование сжатия: Для уменьшения размера CSS файлов можно применять метод сжатия, который заключается в замене длинных свойств на их более короткие аналоги. Например, вместо написания padding-top: 10px; padding-right: 20px; padding-bottom: 10px; padding-left: 20px; можно использовать сокращенное свойство padding: 10px 20px;
Эти методы позволяют существенно уменьшить размер CSS файлов, что в свою очередь улучшит производительность веб-сайта и оптимизирует его загрузку. Для достижения наилучших результатов рекомендуется комбинировать различные методики и использовать специализированные инструменты для минимизации файлов CSS.
Заключение
Работа с CSS требует не только знания основных свойств и методов стилизации элементов, но и умения оптимизировать файлы для обеспечения быстрой загрузки веб-страниц. Соблюдение оптимизационных правил и использование современных подходов к разработке помогут создать эффективные и профессиональные веб-сайты.
Optimizing CSS selectors for faster rendering
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a powerful tool for web developers to style their websites and make them visually appealing to users. However, poorly optimized CSS can lead to slower rendering times and drag down the performance of your website. One of the key factors that can impact the performance of your CSS is the use of selectors.
What are CSS selectors?
CSS selectors are patterns used to select the elements you want to style on a web page. They allow you to target specific HTML elements based on their attributes, classes, ids, and relationships to other elements. While CSS selectors are essential for styling your website, using too many complex selectors can slow down the rendering process.
Why optimize CSS selectors?
Optimizing CSS selectors is crucial for improving the performance of your website. When a browser parses through your CSS to apply styles to elements on a page, it reads selectors from right to left. The browser matches the rightmost selector first and then traverses up the DOM tree to find matching elements. This process can become slow if you have overly complex selectors or inefficiently structured CSS.
Best practices for optimizing CSS selectors
- Use specific selectors: Instead of using universal selectors (*), which target all elements on a page, use more specific selectors to target only the elements you need to style. This will reduce the number of elements the browser has to traverse to find matching elements.
- Avoid descendant selectors: Descendant selectors (e.g., .parent .child) target elements that are descendants of another element. These selectors can be slow to process, especially if they are deep in the DOM tree. Try to limit the use of descendant selectors in your CSS.
- Avoid unnecessary nesting: Nesting selectors inside other selectors can result in overly complex and inefficient CSS. Keep your selectors flat and avoid unnecessary nesting to improve rendering times.
- Avoid using IDs in selectors: IDs have a higher specificity than classes, which can lead to unintended style overrides. Avoid using IDs in your selectors and opt for class names instead for more modular and maintainable CSS.
- Optimize for performance: Consider using performance optimization tools like CSS linting tools or browser developer tools to identify and remove redundant selectors in your CSS. This will help streamline your stylesheets and improve rendering times.
Conclusion
Optimizing CSS selectors is essential for improving the performance of your website. By following best practices such as using specific selectors, avoiding descendant selectors, and optimizing for performance, you can streamline your CSS and ensure faster rendering times for your users. Remember to regularly review and refactor your CSS to keep it clean, efficient, and optimized for performance.
Utilizing CSS preprocessors for better performance
CSS preprocessors are powerful tools that can help streamline your coding process and improve the performance of your website. By using a preprocessor, you can write cleaner, more organized code and take advantage of advanced features that are not available in standard CSS.
There are several popular CSS preprocessors available, such as Sass, Less, and Stylus. Each preprocessor has its own unique syntax and features, but they all share common benefits that can significantly enhance your workflow.
One of the key advantages of using a CSS preprocessor is the ability to use variables. With variables, you can define commonly used values such as colors, font sizes, and margins in one place and easily reuse them throughout your stylesheet. This not only makes your code more efficient, but also makes it easier to update and maintain in the future.
Another useful feature of CSS preprocessors is mixins. Mixins allow you to define reusable blocks of styles that can be applied to multiple elements. This can help reduce the amount of duplicate code in your stylesheet and make your CSS more modular and easier to manage.
In addition to variables and mixins, CSS preprocessors also offer features such as nesting, functions, and inheritance. Nesting allows you to write nested selectors in a more intuitive way, making your code easier to read and understand. Functions enable you to perform calculations and manipulate values dynamically, while inheritance lets you extend styles from one class to another, saving you time and effort.
By taking advantage of these advanced features, you can write more efficient, maintainable, and scalable CSS code that performs better on your website. CSS preprocessors also help reduce the amount of code you need to write, leading to smaller file sizes and faster load times for your web pages.
In conclusion, utilizing CSS preprocessors can greatly enhance the performance of your website by improving the way you write and manage your stylesheets. By adopting a preprocessor into your workflow, you can take your CSS skills to the next level and create more efficient and effective web designs.
Implementing lazy loading for improved website speed
Lazy loading is a technique that can significantly improve website performance by only loading the assets that are currently in the viewport of the user's browser. This means that images, videos, and other media are only loaded when they are needed, reducing the initial load time of the page and improving the overall speed and responsiveness of the website.
There are several ways to implement lazy loading on a website, but one of the most popular methods is to use the "Intersection Observer" API in CSS. This API allows developers to track when an element enters or exits the viewport, and trigger an action (such as loading an image) when this happens.
To implement lazy loading using the Intersection Observer API, follow these steps:
-
Create a placeholder for the lazy-loaded content: Before implementing lazy loading, you will need to create a placeholder for the content that will be loaded lazily. This ensures that the layout of the page does not change when the content is loaded, improving the user experience.
-
Add the "lazy" attribute to the image or video element: In your HTML code, add the "lazy" attribute to the image or video element that you want to load lazily. This tells the browser that this element should only be loaded when it is in the viewport.
-
Use CSS to set the initial state of the lazy-loaded element: In your CSS code, set the initial state of the lazy-loaded element to be hidden or with a low opacity. This ensures that the element is not visible until it is loaded in the viewport.
-
Implement the Intersection Observer API in your JavaScript code: Finally, use the Intersection Observer API in your JavaScript code to track when the lazy-loaded element enters the viewport. When this happens, trigger an action to load the element, such as setting its opacity to 1 or displaying it on the page.
By implementing lazy loading on your website, you can significantly improve the speed and performance of your site, leading to a better user experience and potentially higher rankings in search engine results. Consider using the Intersection Observer API in CSS to easily implement lazy loading and reap the benefits of improved website speed.